Investigating the effectiveness of new topical medications for eczema skin conditions
In this blog, we have discussed what eczema is, its causes, symptoms, and potential treatments for eczema. This blog aims to help individuals manage their condition effectively, alleviate itching, and improve their quality of life.
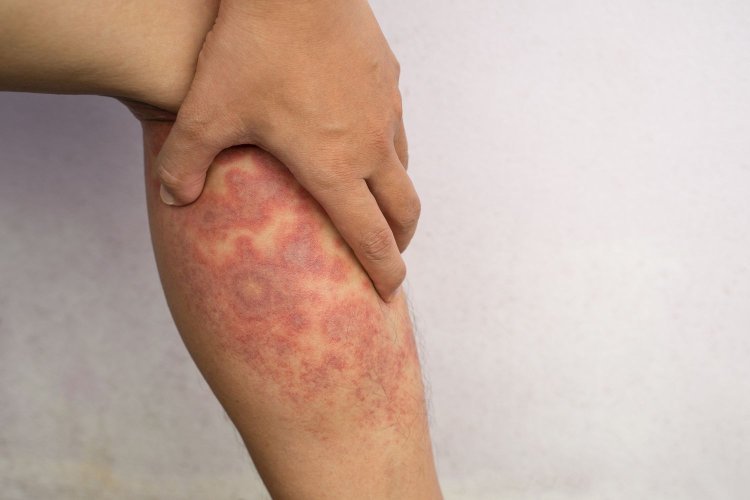
Eczema is a skin condition characterized by itchy, red, and dry skin. It affects millions of people, and its symptoms can be challenging to live with. Eczema can interfere with daily activities and cause significant distress, making effective treatment essential for symptom management and relief.
In this blog, we will discuss what eczema is, its causes, symptoms, and potential treatments for eczema. This blog aims to help individuals manage their condition effectively, alleviate itching, and improve their quality of life.
What is Eczema?
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition that leads to inflammation, redness, and itching. It can appear anywhere on the body but is mostly found on the hands, feet, face, neck, and inside the elbows and knees.
Furthermore, the severity of eczema can vary from person to person, ranging from mild patches of dry skin to severe, widespread inflammation with intense itching and discomfort. Eczema often begins in childhood, but it can occur at any age. While there is no cure for eczema, various treatments can help manage the symptoms and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Causes of Eczema
The exact cause of eczema is not entirely understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Here are some key factors that contribute to the development of eczema:
- Genetics: Eczema often runs in families, suggesting a genetic predisposition. Individuals with a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop the condition.
- Immune System: Eczema is linked to an overactive immune response to environmental triggers. This heightened immune activity causes the skin to become inflamed and irritated.
- Weakened Skin Barrier: People with eczema have a weakened skin barrier, which allows moisture to escape and makes the skin more susceptible to irritants, allergens, and infections. This barrier dysfunction can lead to dry, cracked skin that is prone to inflammation.
- Environmental Triggers: Various environmental factors can trigger or worsen eczema symptoms. Common triggers include:
- Harsh soaps and detergents
- Extreme temperatures and humidity levels
- Allergens such as pollen, pet dander, and dust mites
- Stress and emotional factors
- Certain foods, in some cases
Eczema Risk Factors
Risk factors for eczema include a family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever, indicating a genetic predisposition. Individuals with a weakened skin barrier, which can be due to genetic factors or environmental exposure, are more susceptible.
Additionally, environmental triggers such as harsh soaps, detergents, extreme temperatures, humidity levels, allergens, and stress can also increase the risk. Additionally, having other atopic conditions or a compromised immune system can make one more prone to developing eczema.
Symptoms
Eczema symptoms can vary widely depending on the age of the individual and the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include:
- Itching: Intense itching is often the most distressing symptom of eczema. Scratching can further damage the skin and lead to a cycle of itching and scratching.
- Redness and Inflammation: Affected areas of the skin become red and inflamed, which can be uncomfortable and painful.
- Dry, Scaly Skin: The skin often becomes dry, scaly, and rough. This dryness can lead to cracking and fissuring, especially on the hands and feet.
- Blisters and Oozing: In some cases, eczema can cause small, fluid-filled blisters that can burst and ooze, leading to crusting and potential infection.
- Thickened Skin: Chronic scratching and rubbing can cause the skin to thicken and become leathery, a condition known as lichenification.
- Hyperpigmentation or Hypopigmentation: Prolonged inflammation can lead to changes in skin color, resulting in areas of hyperpigmentation (darkening) or hypopigmentation (lightening).
Management at Home
There are some managements steps that can be taken to ease the symptoms of eczema at home
- Moisturize: Apply fragrance-free cream or ointment 2 times a day, more if needed. Look for ingredients like petrolatum or shea butter.
- Beat the Itch: Cool compresses or oatmeal baths can soothe itchy skin. Avoid scratching – wear mittens at night if needed. In severe cases, your doctor might prescribe itch relief medication.
- Identify Your Triggers: Food allergies, harsh soaps, or stress can worsen eczema. Keep a diary to track what bothers your skin and try to avoid those things.
Bonus Tips:
- Take cool showers, not hot ones.
- Wear loose, cotton clothes.
- Aim for a good night's sleep.
- There's support out there! Consider joining an eczema group to connect with others who understand.
Treatment Options
Eczema treatment focuses on alleviating symptoms, reducing inflammation, and preventing flare-ups. A cornerstone of eczema management is the use of topical treatments, which are applied directly to the affected skin areas. According to a 2023 study published online by *The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, certain prescription topical skin treatments for atopic dermatitis are more effective than others. These treatments are categorized into five main types.
- Topical corticosteroids: They are classified into seven potency levels, from the most to the least potent, and work by reducing the release of the inflammatory chemical phospholipase A2.
- Topical Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors: block inflammatory signals from entering cells.
- Topical PDE4 inhibitors: These increase the production of phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4), which helps decrease the body's inflammatory response.
- Topical calcineurin inhibitors: suppress the production of chemical messengers that signal the body to boost its defenses.
- Other topical treatments include antibiotics and prescription moisturizers.
Topical corticosteroids, available in varying strengths, are commonly prescribed to decrease inflammation and itching by suppressing the release of inflammatory chemicals. For more persistent cases, topical calcineurin inhibitors can be used to inhibit the immune response and reduce skin inflammation without the long-term side effects associated with steroids. Additionally, topical PDE4 inhibitors and JAK inhibitors represent newer classes of treatments that target specific inflammatory pathways to provide relief.
Therapy Options
Phototherapy is an effective treatment for moderate-to-severe eczema, utilizing ultraviolet (UV) light to modulate the immune system and reduce overreaction. However, due to the potential risks of skin aging and increased skin cancer from excessive UV exposure, doctors carefully administer the lowest possible doses and closely monitor the skin. Phototherapy can be used alone or in combination with topical medications.
There are two primary types of phototherapy;
- UV light therapy: It involves exposing the skin to UVA, UVB, or a combination of both rays in a dermatologist's office, with sessions typically occurring two to five times a week. Sometimes, coal tar is applied to the skin to enhance the treatment's effectiveness.
- PUVA therapy: It is for individuals who have not achieved results with UV therapy alone. It involves taking psoralen, a medication that increases the skin's sensitivity to UVA light, thereby enhancing the therapeutic effects.
Conclusion
There are many effective treatments available for managing eczema, and it can often be managed at home. Eczema is a skin condition that impacts not only an individual's physical health but also their mental well-being.
In addition to over-the-counter and prescription treatments, participating in appropriately paid clinical trials can provide access to new and innovative therapies while contributing to medical research.
What's Your Reaction?










![Blog Submission Sites 2024 [High DA]](https://blognow.co.in/uploads/images/202306/image_100x75_6494a03eaff5e.jpg)
![Article Submission Sites 2023 [High DA & PA]](https://blognow.co.in/uploads/images/202307/image_100x75_64c4181f17036.jpg)
![Classified Submission Sites 2023 [High DA & PR]](https://blognow.co.in/uploads/images/202306/image_100x75_649dcd5260808.jpg)




![Article Submission Sites 2023 [High DA & PA]](https://blognow.co.in/uploads/images/202307/image_750x415_64c4181f08ed5.jpg)
![Classified Submission Sites 2023 [High DA & PR]](https://blognow.co.in/uploads/images/202306/image_750x415_649dcd5247eeb.jpg)
![Blog Submission Sites 2024 [High DA]](https://blognow.co.in/uploads/images/202306/image_750x415_6494a03e96bfa.jpg)
